Pas d'autre illustration
pour le moment 😕
Classification
- Classique : en haut de l\'écran, sous le coeur.
- Phylogénétique :
- Clade 4 : Angiospermes ;
- Clade 3 : Dicotylédones_vraies ;
- Clade 2 : Rosidées ;
- Clade 1 : Fabidées ;
- Ordre APN : Fabales ;
- Famille APN : Fabaceae ;
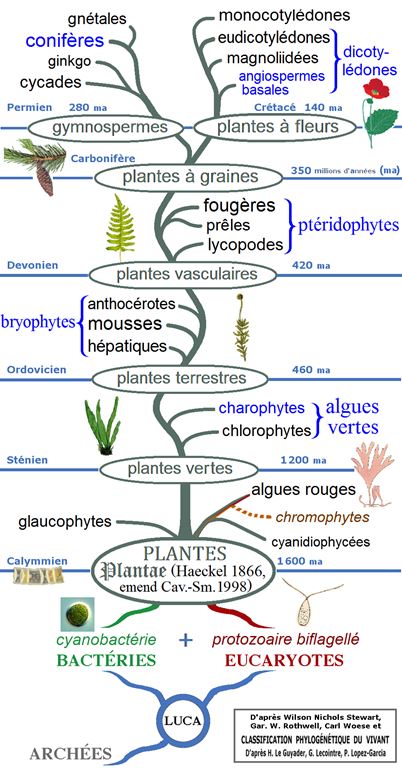
Illustration : cet arbre phylogénétique des plantes montre les principaux clades et groupes traditionnels (monophylétiques en noir et paraphylétiques en bleu).
Dénominations
✖- Nom botanique : Acacia sieberiana DC. (1825)
- Synonymes : Acacia abyssinica sensu auct.(illégitime ou nom invalide ? (qp*)), Acacia amboensis Schinz, Acacia davyi sensu auct. (illégitime ou nom invalide), Acacia purpurascens Vatke 1880, Acacia sieberana DC. (nom invalide [erreur = écriture/orthographe incorrecte/fausse/erronée] ou variante orthographique valide ? (qp*)), Acacia sieberiana DC. subsp. vermoesenii (De Wild.)Troupin, Acacia vermoesenii De Wild. 1925 ;
- Noms anglais et locaux : paperbark acacia, flat-topped thorn
Description et culture
✖ Consommation (rapports de comestibilité, parties utilisables et usages alimentaires correspondants)
Consommation (rapports de comestibilité, parties utilisables et usages alimentaires correspondants)
✖
Tronc (sève : gomme18,19) comestible.
Détails : Gomme, légume. La gomme est consommée crue{{{0(+x).
Partie testée :
/| Taux d'humidité | Énergie (kj) | Énergie (kcal) | Protéines (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| / | / | / | / |
| Pro- vitamines A (µg) |
Vitamines C (mg) | Fer (mg) | Zinc (mg) |
| / | / | / | / |
 Risques et précautions à prendre
Risques et précautions à prendre
✖
néant, inconnus ou indéterminés.
Galerie(s)
✖
Par Chris Fagg (World AgroForestry Centre), via wikimedia
Liens, sources et/ou références
✖Sources et/ou références :
18"World Agroforestry Centre : Agro ForestryTree Database" (en anglais) ; 19PlantZAfrica (en anglais) ; Wikipedia (en anglais) ;
dont classification : "The Plant List" (en anglais) ; "GRIN" (en anglais) ; 69Xycol ;
dont livres et bases de données : 0"Food Plants International" (en anglais) ;
dont biographie/références de "FOOD PLANTS INTERNATIONAL" :
Addis, G., et al, 2005, Ethnobotanical Study of Edible Wild Plants in Some Selected Districts of Ethiopia. Human Ecology, Vol. 33, No. 1, pp. 83-118 ; Ambasta S.P. (Ed.), 2000, The Useful Plants of India. CSIR India. p 7 ; Bekele-Tesemma A., Birnie, A., & Tengnas, B., 1993, Useful Trees and Shrubs for Ethiopia. Regional Soil Conservation Unit. Technical Handbook No 5. p 66 ; Dharani, N., 2002, Field Guide to common Trees & Shrubs of East Africa. Struik. p 36 ; Drummond, R. B., 1981, Common Trees of the Central Watershed Woodlands of Zimbabwe, National Herbarium Salisbury. p 54 ; Fowler, D. G., 2007, Zambian Plants: Their Vernacular Names and Uses. Kew. p 33 ; Grubben, G. J. H. and Denton, O. A. (eds), 2004, Plant Resources of Tropical Africa 2. Vegetables. PROTA, Wageningen, Netherlands. p 559 ; ILDIS Legumes of the World http:www;ildis.org/Legume/Web ; Joffe, P., 2007, Creative Gardening with Indigenous Plants. A South African Guide. Briza. p 133 ; Katende, A.B., Birnie, A & Tengnas B., 1995, Useful Trees and Shrubs for Uganda. Identification, Propagation and Management for Agricultural and Pastoral Communities. Technical handbook No 10. Regional Soil Conservation Unit, Nairobi, Kenya. p 52 ; Maydell, H. von, 1990 Trees and shrubs of the Sahel: their characteristics and uses. Margraf. p 141 ; Palgrave, K.C., 1996, Trees of Southern Africa. Struik Publishers. p 251 ; Palmer, E and Pitman, N., 1972, Trees of Southern Africa. Vol. 2. A.A. Balkema, Cape Town p 700 ; Prodr. 2:463. 1825 ; Roodt, V., 1998, Trees & Shrubs of the Okavango Delta. Medicinal Uses and Nutritional value. The Shell Field Guide Series: Part 1. Shell Botswana. p 195 ; Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew (1999). Survey of Economic Plants for Arid and Semi-Arid Lands (SEPASAL) database. Published on the Internet; https://www.rbgkew.org.uk/ceb/sepasal/internet [Accessed 27th April 2011] (As Acacia sieberiana var. woodii) ; Storrs, A. E. C., 1995 reprint, Know Your Trees. Some Common Trees found in Zambia, Forestry Division. p 47 ; van Wyk, B, van Wyk, P, and van Wyk B., 2000, Photographic guide to Trees of Southern Africa. Briza. p 43 ; Venter, F & J., 2009, Making the most of Indigenous Trees. Briza. p 30 ; www.worldagroforestrycentre.org/sea/products/afdbases/af/asp
Recherche de/pour :
- "Acacia sieberiana" sur Google (pages et
images) ;
TROPICOS (en anglais) ;
Tela Botanica ;
Pl@ntNet ;
Pl@ntUse ;
- "Acacia des oueds{{{69" sur Google (pages, images et recettes) ;
- "Acacia sieberiana" sur Google (pages et
images) ;
TROPICOS (en anglais) ;
Tela Botanica ;
Pl@ntNet ;
Pl@ntUse ;
Sous-espèces, variétes...
✖1 taxons
Espèces du même genre (Acacia)
✖50 taxons (sur 238)
- Acacia abyssinica Hochst. ex Benth.
- Acacia acatlensis Benth.
- Acacia acradenia F.Muell.
- Acacia acuminata Benth.
- Acacia adoxa Pedley
- Acacia adsurgens Maiden & Blakeley
- Acacia aff. Cuthbertsonii Maiden et Blakely
- Acacia albida
- Acacia ammobia Maconochie
- Acacia ampliceps Maslin
- Acacia amythethophylla Steud. ex A. Rich.
- Acacia anaticeps Tindale
- Acacia ancistrocarpa Maiden & Blakely
- Acacia aneura F.Muell. ex Benth. (Mulga)
- Acacia angustissima (Mill.) Kuntze
- Acacia ankokib (Mill.) Kuntze
- Acacia aromo Hook. & Arn.
- Acacia asak (Forssk.) Willd.
- Acacia ataxacantha DC.
- Acacia aulococarpa
- Acacia auriculiformis A. Cunn. ex Benth.
- Acacia baileyana
- Acacia beauverdiana Ewart & Sharman
- Acacia bidwillii Benth.
- Acacia bilimekii
- Acacia bilimekii
- Acacia bivenosa DC.
- Acacia blakelyi
- Acacia blakelyi
- Acacia brachystachya Benth.
- Acacia burkei Benth.
- Acacia bussei Harms ex B. Y. Sjostedt
- Acacia caffra (Thunb.) Willd.
- Acacia calamifolia (Thunb.) Willd.
- Acacia calcicola Forde & Ising
- Acacia cambagei R.T. Baker
- Acacia catechu (L. f.) Willd.
- Acacia caven
- Acacia choriophylla Benth.
- Acacia chundra (Rottler) Willd.
- Acacia citrinoviridis Tindale & Maslin
- Acacia cochliacantha Humb. & Bonpl. ex Willd.
- Acacia colei Maslin & M.A.J. Thomson
- Acacia complanata A. Cunn. ex Benth.
- Acacia concinna (Willd.) DC
- Acacia concurrens Pedley
- Acacia confusa Merr.
- Acacia constricta A.Gray
- Acacia constricta
- Acacia coriacea DC.
- ...
Espèces de la même famille (Fabaceae)
✖50 taxons (sur 2017)
- Abrus cantoniensis
- Abrus fruticulosus
- Abrus precatorius L.
- Abrus pulchellus Wall. ex Thwaites
- Acacia abyssinica Hochst. ex Benth.
- Acacia acatlensis Benth.
- Acacia acradenia F.Muell.
- Acacia acuminata Benth.
- Acacia adoxa Pedley
- Acacia adsurgens Maiden & Blakeley
- Acacia aff. Cuthbertsonii Maiden et Blakely
- Acacia albida
- Acacia ammobia Maconochie
- Acacia ampliceps Maslin
- Acacia amythethophylla Steud. ex A. Rich.
- Acacia anaticeps Tindale
- Acacia ancistrocarpa Maiden & Blakely
- Acacia aneura F.Muell. ex Benth. (Mulga)
- Acacia angustissima (Mill.) Kuntze
- Acacia ankokib (Mill.) Kuntze
- Acacia aromo Hook. & Arn.
- Acacia asak (Forssk.) Willd.
- Acacia ataxacantha DC.
- Acacia aulococarpa
- Acacia auriculiformis A. Cunn. ex Benth.
- Acacia baileyana
- Acacia beauverdiana Ewart & Sharman
- Acacia bidwillii Benth.
- Acacia bilimekii
- Acacia bilimekii
- Acacia bivenosa DC.
- Acacia blakelyi
- Acacia blakelyi
- Acacia brachystachya Benth.
- Acacia burkei Benth.
- Acacia bussei Harms ex B. Y. Sjostedt
- Acacia caffra (Thunb.) Willd.
- Acacia calamifolia (Thunb.) Willd.
- Acacia calcicola Forde & Ising
- Acacia cambagei R.T. Baker
- Acacia catechu (L. f.) Willd.
- Acacia caven
- Acacia choriophylla Benth.
- Acacia chundra (Rottler) Willd.
- Acacia citrinoviridis Tindale & Maslin
- Acacia cochliacantha Humb. & Bonpl. ex Willd.
- Acacia colei Maslin & M.A.J. Thomson
- Acacia complanata A. Cunn. ex Benth.
- Acacia concinna (Willd.) DC
- Acacia concurrens Pedley
- ...